workshops:hardware_hack_lab
Hardware Hack Lab
Stuff that sits in the Hardware Hack Lab Barcelona.
NodeMCU + Range Sensor
A NodeMCU (ESP8266) connected to a range sensor (HC-SR04)
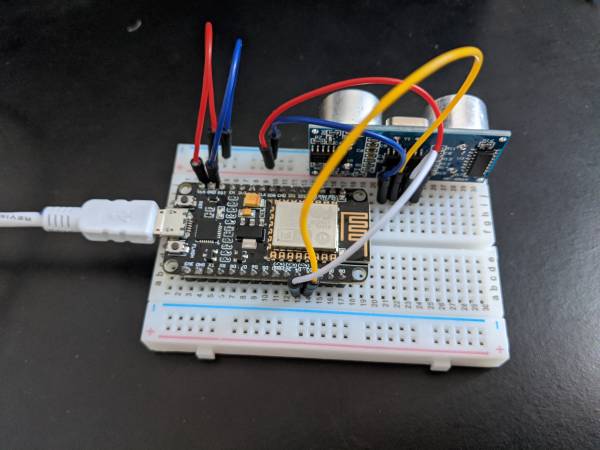
Here are the two tutorials that got me this circuit wired properly:
The key difference with these tutorials and other tutorials found online explaining the same process:
- The GPIO pins are differently ordered on an ESP6288 than on an Arduino.
- Most tutorials with the ESP8266 and HC-SR04 tell you to connect the sensor to 3.3V output from the NodeMCU board, but that did not work at all for me. Connecting to the Vin output port worked because it delivers 5V or close.
Here is the functioning code I used (it requires installation of NewPing library in Arduino IDE):
/* HC-SR04 Basic Demonstration HC-SR04-Basic-Demo.ino Demonstrates functions of HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Range Finder Displays results on Serial Monitor Details: https://dronebotworkshop.com/hc-sr04-ultrasonic-distance-sensor-arduino/ GPIO map for NodeMCU: https://nodemcu.readthedocs.io/en/master/modules/gpio/ */ // Include NewPing Library #include <NewPing.h> #define trigPin 2 #define echoPin 0 #define MAX_DISTANCE 400 NewPing sonar(trigPin, echoPin, MAX_DISTANCE); float duration, distance; int iterations = 5; void setup() { Serial.begin (9600); } void loop() { duration = sonar.ping_median(iterations); // Determine distance from duration // Use 343 metres per second as speed of sound distance = (duration / 2) * 0.0343; // Send results to Serial Monitor Serial.print("Distance = "); if (distance >= 400 || distance <= 2) { Serial.println("Out of range"); } else { Serial.print(distance); Serial.println(" cm"); delay(500); } delay(500); }
workshops/hardware_hack_lab.txt · Last modified: by Julien Deswaef
